Conditional Steps
The Kraken version 1.3 introduces the conditional steps. This feature enables skipping a step under certain conditions. This condition can be based on any data available in the system including the latest data from previous steps.
1.3 release brings several more features - check the release notes.
More details about the conditional steps are below.
The conditional steps rely on lazy step execution. Previously, all
steps were sent to an agent, and the agent executed them all at once
until either all steps were executed or one of the steps failed. Now,
steps are sent from the server to an agent one by one. So, the server
first evaluates the when condition and decides if the step should be
sent for execution to an agent.
The example below shows various cases of when condition:
def stage(ctx):
return {
"parent": "root",
"triggers": {
"parent": True,
},
"parameters": [],
"configs": [],
"jobs": [{
"name": "hello world",
"steps": [{
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "echo 'hello world'"
}, {
"when": "was_no_error",
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "echo 'was_no_error'"
}, {
"when": "was_any_error",
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "echo 'was_any_error'"
}, {
"when": "is_ci",
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "echo 'is_ci'"
}, {
"when": "is_dev",
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "echo 'is_dev'"
}, {
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "missing-command-xyz"
}, {
"when": "was_no_error",
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "echo 'was_no_error 2'"
}, {
"when": "was_any_error",
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "echo 'was_any_error 2'"
}, {
"when": "always",
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "echo 'hello world always' && sleep 5"
}, {
"when": "job.steps[step.index - 1].result.duration > 3",
"tool": "shell",
"cmd": "echo 'hello world #{job.steps[step.index - 1].result}'"
}],
"environments": [{
"system": "any",
"agents_group": "all",
"config": "default"
}]
}]
}
This code can also be found at https://github.com/Kraken-CI/workflow-examples/tree/main/conditional-steps/one.py.
The screenshot below shows the status of these steps execution.
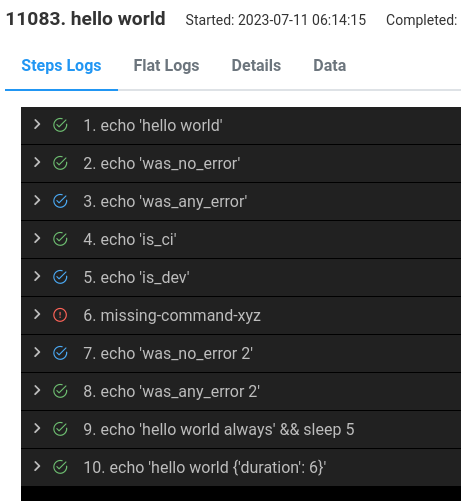
The usage of several built-in variables can be observed, such as
always, is_ci, is_dev, was_no_error, and was_any_error. The
last step presents a more complicated case. It utilizes job.steps
and step.index to verify the outcome of the previous step,
specifically checking if the duration of the previous step was greater
than 3 seconds. If this condition is met, the current step will be
executed.