Webhooks
Overview
Webhooks allow Kraken to integrate with your source code versioning system. This enables automated workflows, such as triggering a Continuous Integration (CI) pipeline when code is pushed or initiating a DEV flow when a pull/merge request is created.
Kraken currently supports webhooks from:
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Gitea
Configuring Webhooks in Kraken
You can configure webhooks in the project settings under the Web Hooks tab. Here, you can enable or disable webhook requests from supported services.
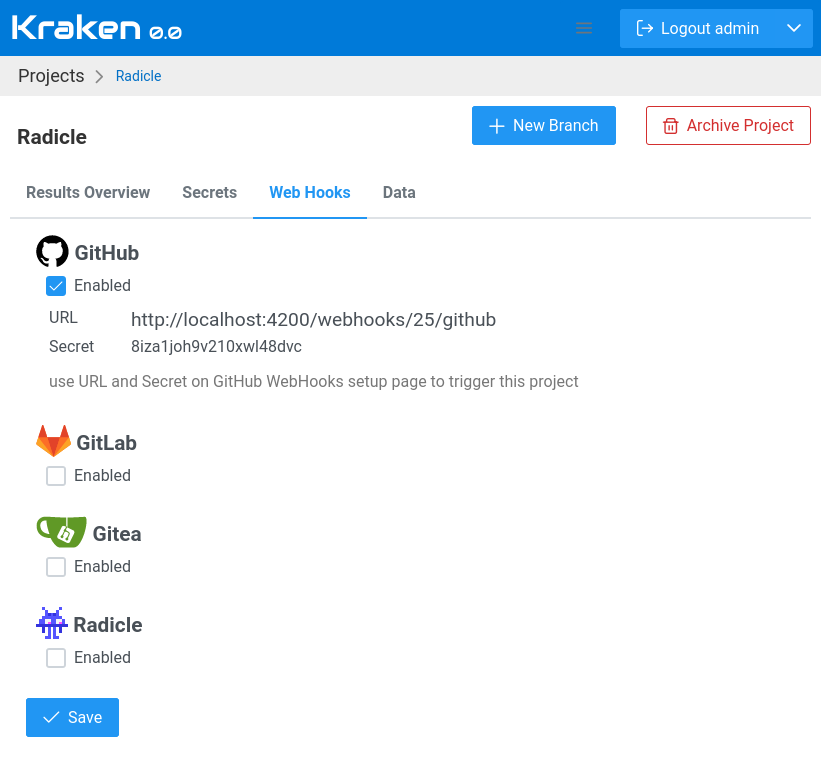
When you enable a webhook for a given Git hosting service, Kraken provides a Webhook URL and a Secret. You need to configure these in your Git hosting provider’s webhook settings.
Setting Up Webhooks in Git Hosting Services
To configure webhooks, navigate to the appropriate settings page in your Git hosting service:
| Git Hosting Service | Webhook Settings Page |
|---|---|
| GitHub | https://github.com/<user>/<project>/settings/hooks |
| GitLab | https://gitlab.com/<user>/<project>/-/hooks |
| Gitea | https://try.gitea.io/<user>/<project>/settings/hooks |
Required Fields
When adding a webhook in your Git hosting service, fill in the following details:
- Payload URL: Use the Webhook URL provided by Kraken.
- Content Type: Set this to
application/json. - Secret or Token: Use the secret provided by Kraken.
- Events to Trigger: Select Let me select individual events, then check:
- Pull Requests
- Pushes
Special Case: Radicle
For Radicle integration, the setup process differs. Refer to the dedicated article: Integration with Radicle.
Testing Webhooks
- Beeceptor: Use Beeceptor to inspect webhook requests by creating an endpoint and replacing Kraken’s Webhook URL with it.
- Pipedream RequestBin: Use Pipedream RequestBin to capture and inspect webhook payloads in real time.