Agents
Agent is a part of Kraken system. The place of agents in Kraken is visualized in Architecture chapter.
Agent is a piece of software that is installed on separate system. It connects to Kraken server, gets jobs to execution and executes them. A job can be executed in several ways. It depends on selected executor indicated in job definition. A job may be executed:
- locally on current host system,
- inside Docker container,
- inside LXD container.
Browsing Agents
In the top bar of UI, on right side, there is an Agents menu.
It can be used to find and manage agents.
The first position, Agents, allows for browsing active agents that
can execute jobs. The table of agents shows their address, the current
system where they are running, whether they are running on a
bare-metal host or in a Docker container, the capabilities of the host
system, and the currently running job, etc.
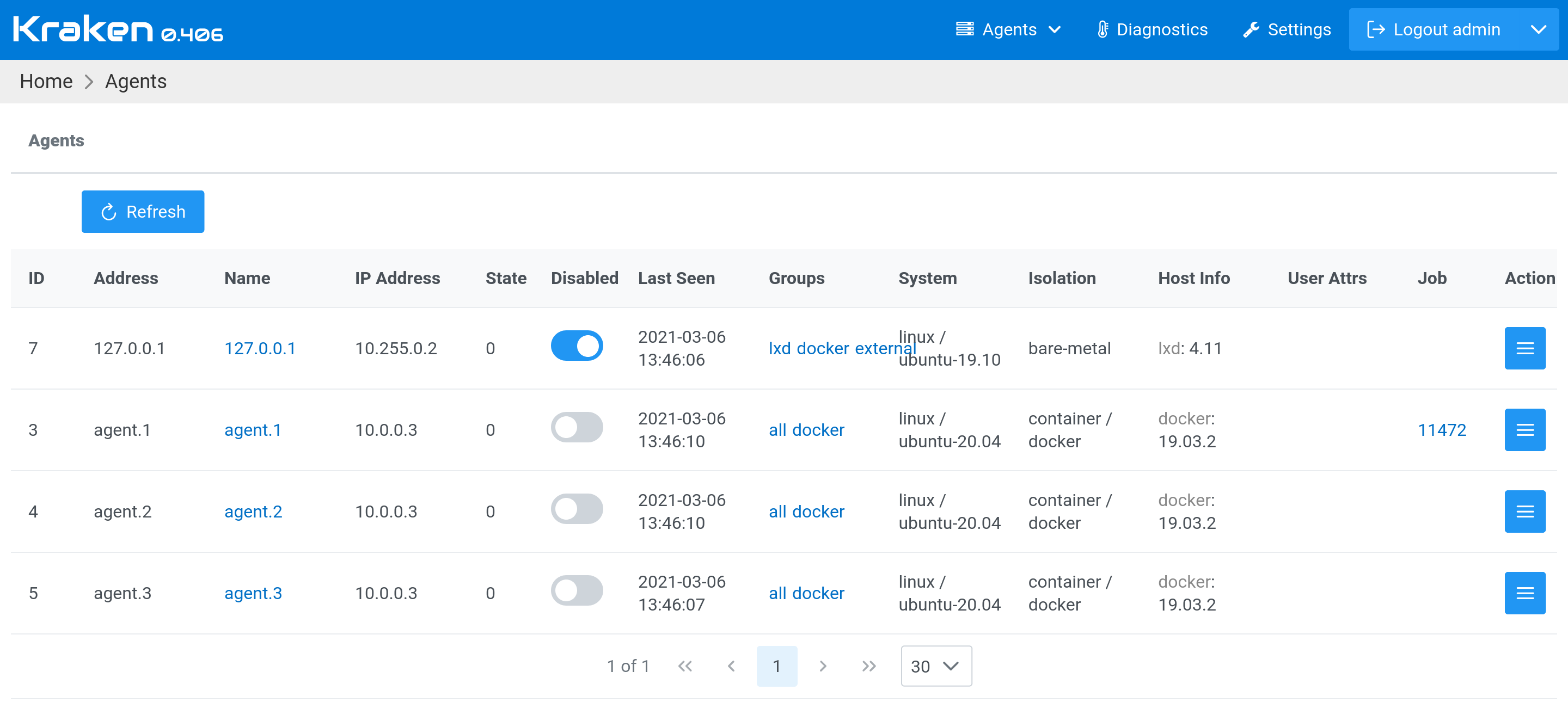
Clicking on the agent address leads to the agent page, which displays
the details of the agent. Here, it is also possible to assign an agent
to Agent Groups. These groups are used in job definitions in the
workflow schema to indicate which group an agent should be selected
from to execute the specified job.
Agents Groups
The next menu option, Groups, allows for organizing agents into
groups. Grouping can be done arbitrarily and managed manually by an
administrator. This can be based on hardware features, host system
capabilities, and so on.
Discovered Agents
The last menu option, Discovered, shows a list of agents that have
tried to connect to the Kraken server but are not authorized to do
so. Here, we can find newly set up agents and authorize them. Once
authorized, these agents can execute jobs, but it is recommended to
assign them to the appropriate groups first.
Setting up a New Agent
There are several methods for setting up a new Kraken Agent. It can be installed on a host system using an installation script. It can be started as a Docker container. It is also possible to copy agent binaries and set it up manually.
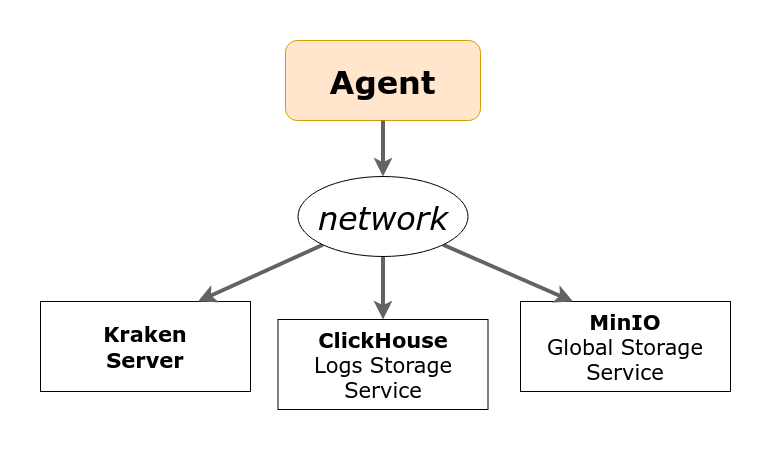
Network Connections
While setting up a new agent, network connections need to be
considered. The Kraken Agent needs to have connections to several
services, which are outlined in the Architecture
chapter. The required services include Kraken Server, MinIO, and ClickHouse.
The address of the server must be passed to the agent binary using the
-s switch or via the KRAKEN_SERVER_ADDR environment variable. This
is handled by the installation script or is already embedded into the
Docker image with Kraken Agent.
In that moment, the addresses of MinIO and ClickHouse should be
acquired from the server. Unfortunately, if the Kraken Server is
started by Docker Compose, then the addresses of these services are
internal, i.e., from a subnet that was created by Docker Compose. The
services are published to the host using defined ports in the Docker
Compose YAML configuration file. Therefore, when the Kraken Agent is
started externally, the addresses for MinIO and ClickHouse need to be
provided manually. This can be done by defining environment variables:
KRAKEN_CLICKHOUSE_ADDR and KRAKEN_MINIO_ADDR. More details about
setting them are provided in the next sections.
Prerequisites
Before installing the Kraken Agent, the system needs to be prepared. Actually, there are two dependencies that need to be installed:
Once these dependencies are installed, we can proceed to install the Kraken Agent.
Installing by a Script
This method relies on an installation script that is hosted on the Kraken server.
Make sure that in the Kraken Web UI, on the Kraken -> Settings page, there is a URL to the Kraken Server set. Please copy and paste the URL from the web browser into this field.
So now, a new agent can be installed. It involves downloading an agent installer and running it. That's all.
The installation script can be downloaded from the Kraken Web UI ->
Agents -> Downloads menu option. There are two options: For Linux
and For Windows.
or via command line using wget - see below.
Agent Install steps:
- Linux
- Windows
- Download Kraken agent installer.
$ wget http://<kraken-server-address>/install/kraken-agent-install.sh
- Execute installer. It will use
sudointernally so it requires rights to invokesudo.
$ chmod a+x kraken-agent-install.sh
$ ./kraken-agent-install.sh
This will download the latest agent from the Kraken server and install
it as a SystemD service on the host. The agent's files are installed
into the /opt/kraken directory. The state of the service can be
checked using systemctl:
$ sudo systemctl status kraken-agent
● kraken-agent.service - Kraken Agent
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/kraken-agent.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2021-03-11 17:09:16 UTC; 1 weeks 0 days ago
Main PID: 699 (python3)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 6998)
Memory: 14.5M
CGroup: /system.slice/kraken-agent.service
└─699 python3 /opt/kraken/kkagent -s http://localhost:6000/ -d /opt/kraken/data run
The Kraken Agent service is running but it may not see MinIO and
ClickHouse services. This can be configured in
/opt/kraken/kraken.env file.
Set KRAKEN_CLICKHOUSE_ADDR to the host where clickhouse-proxy is
running and add its listening port. If Kraken Server is started by
Docker Compose then use the address of the host. The port to
clickhouse-proxy should be taken from .env file or from docker
compose yaml file. Example:
KRAKEN_CLICKHOUSE_ADDR=192.168.0.12:9001.
Set KRAKEN_MINIO_ADDR to the host where minio is running and add
its listening port. If Kraken Server is started by Docker Compose then
use the address of the host. The port to minio should be
taken from .env file or from docker compose yaml file. Example:
KRAKEN_MINIO_ADDR=192.168.0.12:9999.
If Kraken Server was started by docker compose then the ports of these
services can be determined using docker ps. Example:
$ docker ps | grep 'chproxy\|minio'
c17deb0b8fb7 127.0.0.1:5000/kkchproxy:kk_ver .... 0.0.0.0:9001->9001/udp kraken_clickhouse-proxy_1
b3e7c3aeeeb3 minio/minio:RELEASE.2020-12-18T03-27-42Z .... 9000/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9999->9999/tcp kraken_minio_1
where we can see that clickhouse proxy is exposed on 9001 port and
minio on 9999.
- Download Kraken agent installer.
> powershell wget http://<kraken-server-address>/install/kraken-agent-install.bat
- Execute installer. Run it as an
Administrator.
> kraken-agent-install.bat
This will download the latest agent from the Kraken server and install
it as a regular Windows service on the host. The agent's files are installed
into the c:\kraken directory. The state of the service can be
checked in PowerShell:
PS> Get-Service kkagent
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running kkagent kkagent
Now the new agent can be authorized on the Kraken server. On the
"Discovered Agents" page, the IP address of the host with the new
agent should be visible. Select the checkbox and click the Authorize
button. Then, add the agent to the appropriate agent group. Now the
new agent will receive jobs for execution.
Starting in Docker Container
In this case Kraken Agent is packed into Docker image and can be started as Docker container.
The command to start a container is as follows:
$ docker run -e KRAKEN_SERVER_ADDR=<host-addr>:6363 \
-e KRAKEN_CLICKHOUSE_ADDR=<host-addr>:9001 \
-e KRAKEN_MINIO_ADDR=<host-addr>:9999 \
--rm \
us-docker.pkg.dev/kraken-261806/kkagent:<version>
where <host-addr> is a host address where given service is running.
If Kraken Server was started by docker-compose then the
<host-addr> is an address of the host where docker-compose has been
started. The ports above are default ports if the ports where changed
e.g. in docker compose .env file then the same ones should be used
here.
us-docker.pkg.dev/kraken-261806/kkagent:<version> is a location of Docker
image with Kraken Agent. The <version> identifies particular Kraken
version. The latest Kraken <version> can be found on a Kraken's
releases page in GitHub: https://github.com/Kraken-CI/kraken/releases.
Example image URL: us-docker.pkg.dev/kraken-261806/kkagent:0.406. Notice
that the version in the image URL does not have v prefix as on
GitHub page (v0.406).
Starting in Docker Compose from QuickStart
It is also possible to extend Docker Compose from QuickStart and add there an agent or more.
There is already defined one built-in agent. But first, several modifications are needed to solve IP addressing issues. The problem is that it may get a different IP address after a container restart than before. Kraken Server requires that the addresses do not change otherwise it is not possible to identify agents by the Kraken Server.
First, open your compose file (e.g. kraken-docker-compose-X.Y.yaml)
and enable IP Address Management (IPAM) in the lab_net where all
agents reside:
...
lab_net:
driver: bridge
# add the following lines at the end of compose file
ipam:
config:
- subnet: 172.20.0.0/16
Here is added a subnet with particular addresses class,
172.20.0.0/16. You can define any subnet definition you need.
And now add extra agents by copy-pasting agent service:
agent1:
restart: always
image: us-docker.pkg.dev/kraken-261806/kk/kkagent:0.998
environment:
- KRAKEN_CLICKHOUSE_ADDR
- KRAKEN_SERVER_ADDR
networks:
lab_net:
ipv4_address: 172.20.0.11
depends_on:
- server
- minio
- clickhouse-proxy
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
Important things:
- New agent service name should be different e.g.
agent1,agent2, etc. - Remove
- KRAKEN_AGENT_BUILTIN=1environment variable that can be only in one agent. - Add explicit IP address in
networkssection:ipv4_address: 172.20.0.11. Every new agent needs to have a different IP address.
Before running such a modified compose file, shut down the currently
running compose and delete lab_net. To delete this network, first,
check if it exists:
$ docker network ls
It should have name like this <current-folder-name>_lab_net. Please delete it:
$ docker network rm <current-folder-name>_lab_net
Now you can start Docker Compose again. lab_net network will be
recreated with proper new settings:
$ docker-compose --env-file kraken-X.Y.env -f kraken-docker-compose-X.Y.yaml up
Go to Discovered Agents page in Kraken Web UI and check if new agents are present there.